Spring Boot的自动配置机制是其核心特性之一,旨在减少开发人员的配置工作。通过自动配置,Spring Boot可以根据项目依赖和环境配置自动地配置Spring应用。
从@SpringBootApplication开始
用于测试的启动类代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootApplicationG {
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
SpringApplication . run ( SpringBootApplicationG . class , args );
}
}
SpringBoot启动类的入口注解@SpringBootApplication
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
@Target ( ElementType . TYPE )
@Retention ( RetentionPolicy . RUNTIME )
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan (
excludeFilters = {
@Filter ( type = FilterType . CUSTOM , classes = TypeExcludeFilter . class ),
@Filter ( type = FilterType . CUSTOM , classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter . class )
}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
// ...
}
@SpringBootApplication注解实际上等价于使用下面三个注解:
@SpringBootConfiguration@EnableAutoConfiguration@ComponentScan
所以上面的启动类代码也可以改成下面的样子启动:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan (
excludeFilters = {
@Filter ( type = FilterType . CUSTOM , classes = TypeExcludeFilter . class ),
@Filter ( type = FilterType . CUSTOM , classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter . class )
}
)
public class SpringBootApplicationG {
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
SpringApplication . run ( SpringBootApplicationG . class , args );
}
}
其中起到自动配置类作用的就是@EnableAutoConfiguration,看名字就知道“打开自动配置功能“。但是如果我们去掉@EnableAutoConfiguration注解之后就会抛出下面的异常了,无法启动web server,找不到ServletWebServerFactory这个bean。
1
2
org . springframework . context . ApplicationContextException : Unable to start web server ; nested exception is org . springframework . context . ApplicationContextException : Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing ServletWebServerFactory bean .
at org . springframework . boot . web . servlet . context . ServletWebServerApplicationContext . onRefresh ( ServletWebServerApplicationContext . java : 148 ) ~[ main / : na ]
Tomcat自动配置
进入run()方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run ( String ... args ) {
// ...
// 刷新Spring容器, 会解析配置类、扫描、启动WebServer
refreshContext ( context );
// ...
}
进入refreshContext(context)方法:
1
2
3
protected void refresh ( ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext ) {
applicationContext . refresh ();
}
该方法内部会调用applicationContext.refresh()方法,直接就触发了Spring容器的刷新机制,而在Spring容器的刷新过程中,留有一个一个扩展口,留给其他容器来扩展的方法:onRefresh();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public void refresh () throws BeansException , IllegalStateException {
synchronized ( this . startupShutdownMonitor ) {
// ...
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh ();
// ...
}
}
而在SpringBoot中对该方法的实现正视在ServletWebServerApplicationContext中实现的,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
@Override
protected void onRefresh () {
super . onRefresh ();
try {
// ☆ ->
// 启动tomcat
createWebServer ();
} catch ( Throwable ex ) {
throw new ApplicationContextException ( "Unable to start web server" , ex );
}
}
从上面的代码中可以知道,启动WebServer的入口从这里开始。
ServletWebServerApplicationContext.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
private void createWebServer () {
WebServer webServer = this . webServer ;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext ();
if ( webServer == null && servletContext == null ) {
StartupStep createWebServer = this . getApplicationStartup (). start ( "spring.boot.webserver.create" );
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory ();
createWebServer . tag ( "factory" , factory . getClass (). toString ());
this . webServer = factory . getWebServer ( getSelfInitializer ());
createWebServer . end ();
getBeanFactory (). registerSingleton ( "webServerGracefulShutdown" , new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle ( this . webServer ));
getBeanFactory (). registerSingleton ( "webServerStartStop" , new WebServerStartStopLifecycle ( this , this . webServer ));
} else if ( servletContext != null ) {
try {
getSelfInitializer (). onStartup ( servletContext );
} catch ( ServletException ex ) {
throw new ApplicationContextException ( "Cannot initialize servlet context" , ex );
}
}
initPropertySources ();
}
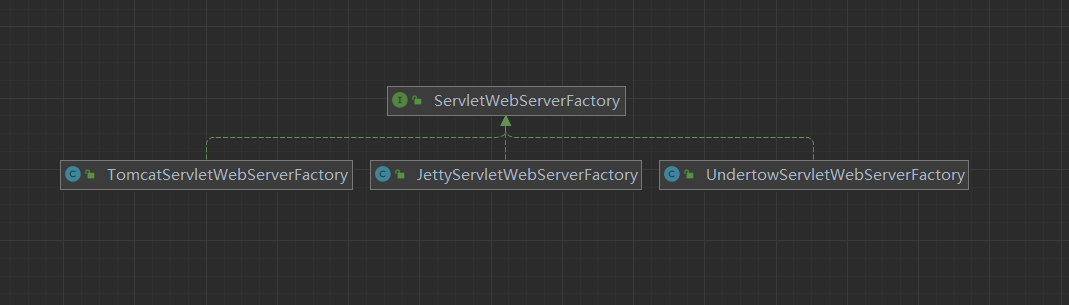
ServletWebServerFactory
从这个接口的实现关系可以看到,对应的正好是SpringBoot所自带支持的三种web容器:
TomcatServletWebServerFactoryJettyServletWebServerFactoryUndertowServletWebServerFactory
这三个Factory中户创建并启动web容器。比如TomcatServletWebServerFactory:
TomcatServletWebServerFactory.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer ( ServletContextInitializer ... initializers ) {
if ( this . disableMBeanRegistry ) {
Registry . disableRegistry ();
}
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat ();
File baseDir = ( this . baseDirectory != null ) ? this . baseDirectory : createTempDir ( "tomcat" );
tomcat . setBaseDir ( baseDir . getAbsolutePath ());
for ( LifecycleListener listener : this . serverLifecycleListeners ) {
tomcat . getServer (). addLifecycleListener ( listener );
}
Connector connector = new Connector ( this . protocol );
connector . setThrowOnFailure ( true );
tomcat . getService (). addConnector ( connector );
customizeConnector ( connector );
tomcat . setConnector ( connector );
tomcat . getHost (). setAutoDeploy ( false );
configureEngine ( tomcat . getEngine ());
for ( Connector additionalConnector : this . additionalTomcatConnectors ) {
tomcat . getService (). addConnector ( additionalConnector );
}
prepareContext ( tomcat . getHost (), initializers );
return getTomcatWebServer ( tomcat );
}
protected TomcatWebServer getTomcatWebServer ( Tomcat tomcat ) {
return new TomcatWebServer ( tomcat , getPort () >= 0 , getShutdown ());
}
getWebServer()该方法中对Tomcat的部分参数进行了设置。
getTomcatWebServer()方法中创建了一个TomcatWebServer对象,在该对象的构造方法中会调用initialized()方法,最总会走到this.tomcat.start();方法正式启动Tomcat容器。
如何选择容器
在上面提到的ServletWebServerApplicationContext#createWebServer这个方法中有一个getWebServerFactory()方法会去从Spring容器中获取ServletWebServerFactory自动配置类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
protected ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory () {
String [] beanNames = getBeanFactory (). getBeanNamesForType ( ServletWebServerFactory . class );
if ( beanNames . length == 0 ) {
throw new ApplicationContextException ( "Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing ServletWebServerFactory bean." );
}
if ( beanNames . length > 1 ) {
throw new ApplicationContextException ( "Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to multiple ServletWebServerFactory beans : " + StringUtils . arrayToCommaDelimitedString ( beanNames ));
}
return getBeanFactory (). getBean ( beanNames [ 0 ] , ServletWebServerFactory . class );
}
根据ServletWebServerFactory这个名字,按规律全局搜索可以找到一个ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,这是一个自动配置类:
从这个自动配置类中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
@Configuration ( proxyBeanMethods = false )
@AutoConfigureOrder ( Ordered . HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE )
@ConditionalOnClass ( ServletRequest . class )
@ConditionalOnWebApplication ( type = Type . SERVLET )
@EnableConfigurationProperties ( ServerProperties . class )
@Import ({
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration . BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar . class ,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration . EmbeddedTomcat . class ,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration . EmbeddedJetty . class ,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration . EmbeddedUndertow . class
})
public class ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration {
// ....
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false):声明这是一个配置类,并禁用代理 bean 方法以提高性能。
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE):设置自动配置的顺序为最高优先级,以确保此配置在其他自动配置之前应用。
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRequest.class):仅在类路径上存在 ServletRequest 类时才启用此配置,确保这是一个 Servlet 环境。
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET):仅在应用程序类型为 Servlet 的 Web 应用时才启用此配置。
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class):启用 ServerProperties 配置属性,以便于通过配置文件(如 application.properties 或 application.yml)进行配置。
@Import:导入其他必要的配置类:
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar:用于注册 BeanPostProcessor。
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat:嵌入式 Tomcat 配置。
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedJetty:嵌入式 Jetty 配置。
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedUndertow:嵌入式 Undertow 配置。
其中ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat和其他两个都是静态内部类,内容如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
@Configuration ( proxyBeanMethods = false )
@ConditionalOnClass ({ Servlet . class , Tomcat . class , UpgradeProtocol . class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean ( value = ServletWebServerFactory . class , search = SearchStrategy . CURRENT )
static class EmbeddedTomcat {
@Bean
TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcatServletWebServerFactory (
ObjectProvider < TomcatConnectorCustomizer > connectorCustomizers ,
ObjectProvider < TomcatContextCustomizer > contextCustomizers ,
ObjectProvider < TomcatProtocolHandlerCustomizer <?>> protocolHandlerCustomizers
) {
TomcatServletWebServerFactory factory = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory ();
factory . getTomcatConnectorCustomizers (). addAll ( connectorCustomizers . orderedStream (). collect ( Collectors . toList ()));
factory . getTomcatContextCustomizers (). addAll ( contextCustomizers . orderedStream (). collect ( Collectors . toList ()));
factory . getTomcatProtocolHandlerCustomizers (). addAll ( protocolHandlerCustomizers . orderedStream (). collect ( Collectors . toList ()));
return factory ;
}
}
当容器中存在下面的情况的时候才会想Spring中注册tomcatServletWebServerFactory这个Bean:
类加载路径中中存在Servlet.class,Tomcat.class, UpgradeProtocol.class这三个class。
容器中不存在ServletWebServerFactory。
同时在参数中需要依赖于三个参数TomcatConnectorCustomizer,TomcatContextCustomizer,TomcatProtocolHandlerCustomizer,
这些类都是用来自定义Tomcat的,用法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
@Bean
public TomcatConnectorCustomizer tomcatConnectorCustomizer () {
return new TomcatConnectorCustomizer () {
@Override
public void customize ( org . apache . catalina . connector . Connector connector ) {
connector . setPort ( 9123 );
}
};
}
// 启动日志输出:
// Tomcat started on port ( s ): 9123 ( http ) with context path ''
这样可以对Tomcat的一些配置进行自定义,但是我们一般在yaml文件中配置,而不是使用这种方式。
这样配置为什么能起到作用呢,那就需要去看下这些Customizer的后续逻辑了。在上面提到的getWebServer()这个方法中有一个customizeConnector(connector);方法,进入这个方法之后,在这个方法的底部我们可以看到,调用了所有的ConnectCustomizer的customize()方法进行了属性设置,这里会覆盖掉yaml文件中的配置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer ( ServletContextInitializer ... initializers ) {
// ...
customizeConnector ( connector );
tomcat . setConnector ( connector );
tomcat . getHost (). setAutoDeploy ( false );
// ...
prepareContext ( tomcat . getHost (), initializers );
return getTomcatWebServer ( tomcat );
}
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration除了会导入三个和容器类,还会加入一个Registar:就是ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar,那么Spring在启动的时候就会调用该类的registerBeanDefinitions()方法,而它的这个方法又向容器中注册了一个BeanPostProcessor:WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor。
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar#registerBeanDefinitions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions ( AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata ,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry ) {
if ( this . beanFactory == null ) {
return ;
}
registerSyntheticBeanIfMissing (
registry , "webServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor" ,
WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor . class ,
WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor :: new
);
registerSyntheticBeanIfMissing (
registry ,
"errorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor" ,
ErrorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor . class ,
ErrorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor :: new
);
}
当WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor被注册成功之后,Spring就会在启动过程中的Bean的初始化之前或者之后来调用它的对应的方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization ( Object bean , String beanName ) throws BeansException {
return bean ;
}
@SuppressWarnings ( "unchecked" )
private void postProcessBeforeInitialization ( WebServerFactory webServerFactory ) {
LambdaSafe . callbacks (
WebServerFactoryCustomizer . class ,
getCustomizers (),
webServerFactory
)
. withLogger ( WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor . class )
. invoke (
// ☆ ->
// ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer 读取配置配置文件中server相关的
( customizer ) -> customizer . customize ( webServerFactory )
);
}
从上面的代码中可以看出来,后置方法没有逻辑,而前置方法做的主要内容就是调用ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer.customize()方法,来完成server相关的配置读取和设置。
条件注解
SpringBoot中为我们提供了很多的条件注解,其中主要有下面的几个:
注解
作用
@ConditionalOnBean当指定的 bean 存在时,才会加载当前配置。
@ConditionalOnClass当指定的类存在于类路径时,才会加载当前配置。
@ConditionalOnCloudPlatform当应用程序运行在特定的云平台时,才会加载当前配置。
@ConditionalOnExpression根据 SpEL 表达式的结果来决定是否加载当前配置。
@ConditionalOnJava当运行的 Java 版本满足指定要求时,才会加载当前配置。
@ConditionalOnJndi当指定的 JNDI 资源存在时,才会加载当前配置。
@ConditionalOnMissingBean当指定的 bean 不存在时,才会加载当前配置。
@ConditionalOnMissingClass当指定的类不存在于类路径时,才会加载当前配置。
@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication当当前应用程序不是 Web 应用时,才会加载当前配置。
@ConditionalOnProperty当指定的属性有特定值时,才会加载当前配置。
@ConditionalOnResource当指定的资源存在时,才会加载当前配置。
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate当指定的 bean 在上下文中是唯一候选者时,才会加载当前配置。
@ConditionalOnWarDeployment当应用程序作为 WAR 部署时,才会加载当前配置。
@ConditionalOnWebApplication当当前应用程序是 Web 应用时,才会加载当前配置。
如果只是简单的额需要一个条件注解,我们可以直接继承SpringBootCondition,实际上SpringBootCondition这个类最后还是实现了Condition接口的,然后重写它的match()方法。
在SpringBoot的条件注解中很多并不是直接继承自SpringBootCondition,而是中间还有其他的一些实现类。判断是否满足条件就是在这个类的matches()方法中判断的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public final boolean matches ( ConditionContext context , AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata ) {
// 针对每个条件注解进行条件判断
// 条件注解写在了哪个类上, 或者哪个方法上
String classOrMethodName = getClassOrMethodName ( metadata );
try {
// ☆ ->
// 条件的判断结果
// OnBeanCondition / OnClassCondition
ConditionOutcome outcome = getMatchOutcome ( context , metadata );
// 如果log的日志级别为trace, 则记录当前的判断结果
logOutcome ( classOrMethodName , outcome );
// 将判断结果记录到ConditionEvaluationReport中
// ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener 会在收到ContextRefreshedEvent事件后把判断结果用日志的方式打印出来
recordEvaluation ( context , classOrMethodName , outcome );
return outcome . isMatch ();
} catch ( NoClassDefFoundError ex ) {
throw new IllegalStateException ( "Could not evaluate condition on " + classOrMethodName + " due to " + ex . getMessage () + " not found. Make sure your own configuration does not rely on that class. This can also happen if you are @ComponentScanning a springframework package (e.g. if you put a @ComponentScan in the default package by mistake)" , ex );
} catch ( RuntimeException ex ) {
throw new IllegalStateException ( "Error processing condition on " + getName ( metadata ), ex );
}
}
第10行返回的ConditionOutcome中有两个属性:
boolean match:表示是否能匹配上ConditionMessage message:记录了如果匹配不上,是缺少那些条件。
代码中的getMatchOutcome(context, metadata)是一个模板方法,交个子类去实现的,比如说下面提到的OnClassCondition中的getMatchOutcome()方法。
logOutcome(classOrMethodName, outcome);方法和 recordEvaluation(context, classOrMethodName, outcome);都是和后面Spring启动的完了之后,见听到ContextRefreshedEvent这个事件的时候,会将前面所有记录的logs都打印出来。对应的监听器为ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener。
以上面分析过的这个类:ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration为例子,这个类上有两个条件注解:
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRequest.class)@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
ConditionalOnClass
判断某个类是否存在
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
@Target ({ ElementType . TYPE , ElementType . METHOD })
@Retention ( RetentionPolicy . RUNTIME )
@Documented
@Conditional ( OnClassCondition . class )
public @interface ConditionalOnClass {
/**
* The classes that must be present. Since this annotation is parsed by loading class
* bytecode, it is safe to specify classes here that may ultimately not be on the
* classpath, only if this annotation is directly on the affected component and
* <b>not</b> if this annotation is used as a composed, meta-annotation. In order to
* use this annotation as a meta-annotation, only use the {@link #name} attribute.
* @return the classes that must be present
*/
Class <?>[] value () default {};
/**
* The classes names that must be present.
* @return the class names that must be present.
*/
String [] name () default {};
}
可以看到这个这个注解还是依赖了OnClassCondition,下面进入OnClassCondition类中看一下上面提到的getMatchOutcome()方法是怎么实现的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome ( ConditionContext context , AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata ) {
ClassLoader classLoader = context . getClassLoader ();
ConditionMessage matchMessage = ConditionMessage . empty ();
// 拿到ConditionalOnClass注解中的value值,也就是判断是否存在ConditionalOnClass中配置的条件类名
List < String > onClasses = getCandidates ( metadata , ConditionalOnClass . class );
if ( onClasses != null ) {
// ☆ ->
// 判断onClasses中不存在的类
List < String > missing = filter ( onClasses , ClassNameFilter . MISSING , classLoader );
// 如果有缺失的类,那就表示不匹配
if ( ! missing . isEmpty ()) {
return ConditionOutcome . noMatch ( ConditionMessage . forCondition ( ConditionalOnClass . class ). didNotFind ( "required class" , "required classes" ). items ( Style . QUOTE , missing ));
}
// 否则就表示匹配
matchMessage = matchMessage . andCondition ( ConditionalOnClass . class )
. found ( "required class" , "required classes" )
. items ( Style . QUOTE , filter ( onClasses , ClassNameFilter . PRESENT , classLoader ));
}
// 如果有@ConditionalOnMissingClass注解则继续解析
// 和上面类似,只不过是判断onMissingClasses是不是全部缺失,如果是则表示匹配
List < String > onMissingClasses = getCandidates ( metadata , ConditionalOnMissingClass . class );
if ( onMissingClasses != null ) {
List < String > present = filter ( onMissingClasses , ClassNameFilter . PRESENT , classLoader );
// 判断一下是不是我不想他们存在的那些类都不存在。
if ( ! present . isEmpty ()) {
return ConditionOutcome . noMatch ( ConditionMessage . forCondition ( ConditionalOnMissingClass . class ). found ( "unwanted class" , "unwanted classes" ). items ( Style . QUOTE , present ));
}
matchMessage = matchMessage . andCondition ( ConditionalOnMissingClass . class )
. didNotFind ( "unwanted class" , "unwanted classes" )
. items ( Style . QUOTE , filter ( onMissingClasses , ClassNameFilter . MISSING , classLoader ));
}
return ConditionOutcome . match ( matchMessage );
}
第6行到第22行是在找到ConditionnalOnClass中配置的且不存在类路径中的类名,采用的事反向的方法,这样可以方便的在记录下来有哪些类是没有加载到的,并记录到log中。
filter(onClasses, ClassNameFilter.MISSING, classLoader);中使用的是ClassNameFilter.MISSING的匹配逻辑。代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
protected final List < String > filter (
Collection < String > classNames ,
ClassNameFilter classNameFilter ,
ClassLoader classLoader
) {
if ( CollectionUtils . isEmpty ( classNames )) {
return Collections . emptyList ();
}
List < String > matches = new ArrayList <> ( classNames . size ());
for ( String candidate : classNames ) {
if ( classNameFilter . matches ( candidate , classLoader )) {
matches . add ( candidate );
}
}
return matches ;
}
// matches()方法对应的实现
protected enum ClassNameFilter {
// ...
MISSING {
@Override
public boolean matches ( String className , ClassLoader classLoader ) {
return ! isPresent ( className , classLoader );
}
};
// ...
static boolean isPresent ( String className , ClassLoader classLoader ) {
if ( classLoader == null ) {
classLoader = ClassUtils . getDefaultClassLoader ();
}
try {
resolve ( className , classLoader );
return true ;
} catch ( Throwable ex ) {
return false ;
}
}
}
继续回到getMatchOutcome()方法的26~35行,这里是在看,如果当前类的注解上面除了@ConditionalOnClass还有ConditionalOnMissingClass注解,那么就顺便解析了@ConditionalOnMissingClass。这里比较奇怪,为什么在解析@ConditionalOnClass的注解中还去解析一下@ConditionalOnMissingClass这个注解呢,因为如果按照Spring的解析习惯,两个注解分开来的话,那么SpringBootCondtion.matches()方法就会被执行两次,而且这两个注解的内容比较相似,只是判断条件相反,所以可以顺便解析了。
ConditionalOnBean
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
@Target ({ ElementType . TYPE , ElementType . METHOD })
@Retention ( RetentionPolicy . RUNTIME )
@Documented
@Conditional ( OnBeanCondition . class )
public @interface ConditionalOnBean {
Class <?>[] value () default {};
String [] type () default {};
Class <? extends Annotation >[] annotation () default {};
String [] name () default {};
SearchStrategy search () default SearchStrategy . ALL ;
Class <?>[] parameterizedContainer () default {};
}
Class<?>[] value() default {}:指定需要存在的 bean 类型,当这些类型的 bean 存在时,加载配置。String[] type() default {}:指定需要存在的 bean 类型名称,以字符串形式表示,当这些类型的 bean 存在时,加载配置。Class<? extends Annotation>[] annotation() default {}:指定需要存在的注解类型,当具有这些注解的 bean 存在时,加载配置。String[] name() default {}:指定需要存在的 bean 名称,当这些名称的 bean 存在时,加载配置。SearchStrategy search() default SearchStrategy.ALL:定义在寻找 bean 时的策略。可以是以下几种:
ALL:在当前和所有祖先上下文中查找。CURRENT:仅在当前上下文中查找。ANCESTORS:在当前上下文及其所有祖先上下文中查找。PARENTS:仅在当前上下文的直接父上下文中查找。
Class<?>[] parameterizedContainer() default {}:指定需要存在的参数化容器类型(如 List<User>),当这些类型的 bean 存在时,加载配置。
在ConditionalOnMissingBean中还有下面两个属性:
Class<?>[] ignored() default {};:在匹配的时候需要被忽略掉的bean的类型数组。String[] ignoredType() default {};:在匹配的时候需要忽略掉的bean的名字数组。
类似的进入OnBeanCondition.java看个究竟:
OnBeanCondition.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome ( ConditionContext context , AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata ) {
ConditionMessage matchMessage = ConditionMessage . empty ();
MergedAnnotations annotations = metadata . getAnnotations ();
// 如果存在ConditionalOnBean注解
if ( annotations . isPresent ( ConditionalOnBean . class )) {
Spec < ConditionalOnBean > spec = new Spec <> ( context , metadata , annotations , ConditionalOnBean . class );
MatchResult matchResult = getMatchingBeans ( context , spec );
// 如果某个Bean不存在
if ( ! matchResult . isAllMatched ()) {
String reason = createOnBeanNoMatchReason ( matchResult );
// 直接返回
return ConditionOutcome . noMatch ( spec . message (). because ( reason ));
}
// 所有Bean都存在
matchMessage = spec . message ( matchMessage ). found ( "bean" , "beans" ). items ( Style . QUOTE , matchResult . getNamesOfAllMatches ());
}
// 如果存在ConditionalOnSingleCandidate注解
if ( metadata . isAnnotated ( ConditionalOnSingleCandidate . class . getName ())) {
Spec < ConditionalOnSingleCandidate > spec = new SingleCandidateSpec ( context , metadata , annotations );
MatchResult matchResult = getMatchingBeans ( context , spec );
// 有的bean没有匹配到(不存在) 直接返回
if ( ! matchResult . isAllMatched ()) {
return ConditionOutcome . noMatch ( spec . message (). didNotFind ( "any beans" ). atAll ());
}
// Bean存在
Set < String > allBeans = matchResult . getNamesOfAllMatches ();
// 如果只有一个
if ( allBeans . size () == 1 ) {
matchMessage = spec . message ( matchMessage ). found ( "a single bean" ). items ( Style . QUOTE , allBeans );
} else {
// 如果有多个, 看一下bean上面是否有@Primary注解
List < String > primaryBeans = getPrimaryBeans ( context . getBeanFactory (), allBeans , spec . getStrategy () == SearchStrategy . ALL );
// 没有主Bean,那就不匹配
if ( primaryBeans . isEmpty ()) {
return ConditionOutcome . noMatch ( spec . message (). didNotFind ( "a primary bean from beans" ). items ( Style . QUOTE , allBeans ));
}
// 有多个主Bean,那就不匹配
if ( primaryBeans . size () > 1 ) {
return ConditionOutcome . noMatch ( spec . message (). found ( "multiple primary beans" ). items ( Style . QUOTE , primaryBeans ));
}
// 只有一个主Bean
matchMessage = spec . message ( matchMessage )
. found ( "a single primary bean '" + primaryBeans . get ( 0 ) + "' from beans" )
. items ( Style . QUOTE , allBeans );
}
}
// 存在 ConditionalOnMissingBean 注解
if ( metadata . isAnnotated ( ConditionalOnMissingBean . class . getName ())) {
Spec < ConditionalOnMissingBean > spec = new Spec <> ( context , metadata , annotations , ConditionalOnMissingBean . class );
MatchResult matchResult = getMatchingBeans ( context , spec );
// 有任意一个Bean存在,那就条件不匹配
if ( matchResult . isAnyMatched ()) {
String reason = createOnMissingBeanNoMatchReason ( matchResult );
return ConditionOutcome . noMatch ( spec . message (). because ( reason ));
}
// 都不存在在,则匹配
matchMessage = spec . message ( matchMessage ). didNotFind ( "any beans" ). atAll ();
}
return ConditionOutcome . match ( matchMessage );
}
从上面的代码中看到和之前的OnClassCondition.java一样,在getMatchOutcome()方法中同事处理了下面三个条件:ConditionalOnBean、ConditionalOnSingleCandidate、ConditionalOnMissingBean。
其他的条件注解和上面提到的两个注解逻辑都是差不多的,只是条件不同。
SpringBoot的自动配置
@EnableAutoConfiguration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
@Target ( ElementType . TYPE )
@Retention ( RetentionPolicy . RUNTIME )
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import ( AutoConfigurationImportSelector . class )
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration" ;
Class <?>[] exclude () default {};
String [] excludeName () default {};
}
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};:根据类型排除某些自动配置类String[] excludeName() default {};:根据名字排除某些自动配置类
导入了一个AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class这个类。会来执行这个类中的selectImports()方法,内容如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
@Override
public String [] selectImports ( AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata ) {
// 会在所有@Configuration都解析完了之后才执行, 即在解析完程序员所有的配置类后才会来加载
// springboot自己的自动配置类
if ( ! isEnabled ( annotationMetadata )) {
return NO_IMPORTS ;
}
// ☆ ->
// SPI 获取自动配置类(spring.factories中所导入的)
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry ( annotationMetadata );
// 这里返回的配置类会按照之前的@Condition...的条件一个一个的匹配是否满足
return StringUtils . toStringArray ( autoConfigurationEntry . getConfigurations ());
}
进入getAutoConfigurationEntry()方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry ( AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata ) {
if ( ! isEnabled ( annotationMetadata )) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY ;
}
// 获取@EnableAutoConfiguration的属性
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes ( annotationMetadata );
// 获取spring.factories中所有的AutoConfiguration
List < String > configurations = getCandidateConfigurations ( annotationMetadata , attributes );
// 去重(也就是按类名去重)
configurations = removeDuplicates ( configurations );
// 获取需要排除的AutoConfiguration,可以通过@EnableAutoConfiguration注解的exclude属性,
// 或者spring.autoconfigure.exclude来配置
Set < String > exclusions = getExclusions ( annotationMetadata , attributes );
// 排除
checkExcludedClasses ( configurations , exclusions );
configurations . removeAll ( exclusions );
// ☆ ->
// 获取spring.factories中的AutoConfigurationImportFilter对AutoConfiguration进行过滤
// 默认会拿到OnBeanCondition、OnClassCondition、OnWebApplicationCondition
// 这三个会去判断上面的AutoConfiguration是否符合它们自身所要求的条件,不符合的会过滤掉,表示不会进行解析了
// 会利用spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties中的配置来进行过滤
// spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties文件中的内容是利用Java中的AbstractProcessor技术在[编译]时生成出来的
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter (). filter ( configurations );
// configurations表示合格的,exclusions表示被排除的,
// 把它们记录在ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener中
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents ( configurations , exclusions );
// 最后返回的AutoConfiguration都是符合条件的
return new AutoConfigurationEntry ( configurations , exclusions );
}
getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);,这个方法会读取所有的spring.factories内容。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
private static Map < String , List < String >> loadSpringFactories ( ClassLoader classLoader ) {
Map < String , List < String >> result = cache . get ( classLoader );
// ...
try {
Enumeration < URL > urls = classLoader . getResources ( FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION );
// ...
// Replace all lists with unmodifiable lists containing unique elements
result . replaceAll (( factoryType , implementations ) -> implementations . stream (). distinct ()
. collect ( Collectors . collectingAndThen ( Collectors . toList (), Collections :: unmodifiableList )));
cache . put ( classLoader , result );
} catch ( IOException ex ) {
// ...
}
return result ;
}
先从缓存中拿,如果没有拿到,就会从指定的位置(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories")读取,最后在存储到缓存中中。
拿到了这些自动配置类了之后还有走前面说过的过滤逻辑,getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);是通过这一行代码来实现的,这行代码有两个作用,第一个是获取ClassFilter:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
private ConfigurationClassFilter getConfigurationClassFilter () {
if ( this . configurationClassFilter == null ) {
List < AutoConfigurationImportFilter > filters = getAutoConfigurationImportFilters ();
for ( AutoConfigurationImportFilter filter : filters ) {
invokeAwareMethods ( filter );
}
this . configurationClassFilter = new ConfigurationClassFilter ( this . beanClassLoader , filters );
}
return this . configurationClassFilter ;
}
getAutoConfigurationImportFilters ();
在通过getAutoConfigurationImportFilters();
1
2
3
protected List < AutoConfigurationImportFilter > getAutoConfigurationImportFilters () {
return SpringFactoriesLoader . loadFactories ( AutoConfigurationImportFilter . class , this . beanClassLoader );
}
这个方法会从spring.factories中获取AutoConfigurationImportFilter对应的自动配置类:
1
2
3
4
5
# Auto Configuration Import Filters
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter = \
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnWebApplicationCondition
获取到这三个条件类之后,就会调用filter()方法:
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.ConfigurationClassFilter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
List < String > filter ( List < String > configurations ) {
long startTime = System . nanoTime ();
String [] candidates = StringUtils . toStringArray ( configurations );
boolean skipped = false ;
for ( AutoConfigurationImportFilter filter : this . filters ) {
// ☆ ->
boolean [] match = filter . match ( candidates , this . autoConfigurationMetadata );
for ( int i = 0 ; i < match . length ; i ++ ) {
if ( ! match [ i ] ) {
candidates [ i ] = null ;
skipped = true ;
}
}
}
if ( ! skipped ) {
return configurations ;
}
List < String > result = new ArrayList <> ( candidates . length );
for ( String candidate : candidates ) {
if ( candidate != null ) {
result . add ( candidate );
}
}
if ( logger . isTraceEnabled ()) {
int numberFiltered = configurations . size () - result . size ();
logger . trace ( "Filtered " + numberFiltered + " auto configuration class in "
+ TimeUnit . NANOSECONDS . toMillis ( System . nanoTime () - startTime ) + " ms" );
}
return result ;
}
}
在第8行,调用match()方法之后进入下面
FilteringSpringBootCondition.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
@Override
public boolean [] match ( String [] autoConfigurationClasses , AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata ) {
ConditionEvaluationReport report = ConditionEvaluationReport . find ( this . beanFactory );
// ☆ ->
// autoConfigurationClasses是所有的那100多个
ConditionOutcome [] outcomes = getOutcomes ( autoConfigurationClasses , autoConfigurationMetadata );
boolean [] match = new boolean [ outcomes . length ] ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < outcomes . length ; i ++ ) {
match [ i ] = ( outcomes [ i ] == null || outcomes [ i ] . isMatch ());
if ( ! match [ i ] && outcomes [ i ] != null ) {
logOutcome ( autoConfigurationClasses [ i ] , outcomes [ i ] );
if ( report != null ) {
report . recordConditionEvaluation ( autoConfigurationClasses [ i ] , this , outcomes [ i ] );
}
}
}
return match ;
}
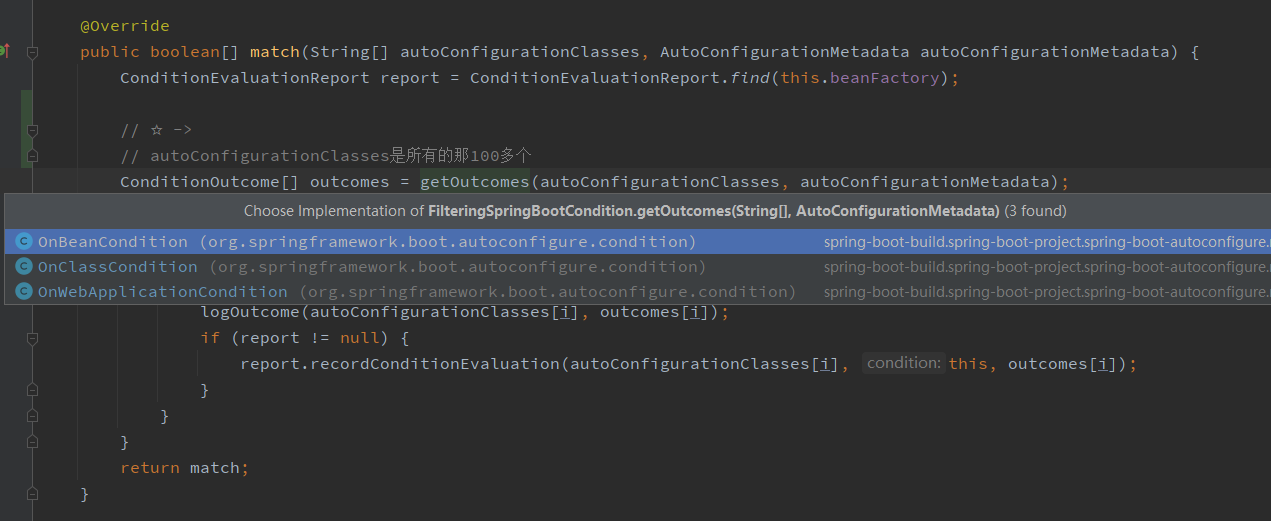
上面getOutcomnes()方法,在OnBeanCondition、OnClassCondition、OnWebApplicationCondition中有实现,如下图所示。
这里以OnClassCondition为例子来看一下,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
@Override
protected final ConditionOutcome [] getOutcomes (
String [] autoConfigurationClasses ,
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata
) {
if ( autoConfigurationClasses . length > 1 && Runtime . getRuntime (). availableProcessors () > 1 ) {
// 如果是多核的会采用多线程去处理
return resolveOutcomesThreaded ( autoConfigurationClasses , autoConfigurationMetadata );
} else {
OutcomesResolver outcomesResolver = new StandardOutcomesResolver ( autoConfigurationClasses , 0 ,
autoConfigurationClasses . length , autoConfigurationMetadata , getBeanClassLoader ());
return outcomesResolver . resolveOutcomes ();
}
}
private ConditionOutcome [] resolveOutcomesThreaded (
String [] autoConfigurationClasses ,
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata
) {
int split = autoConfigurationClasses . length / 2 ;
OutcomesResolver firstHalfResolver = createOutcomesResolver ( autoConfigurationClasses , 0 , split , autoConfigurationMetadata );
OutcomesResolver secondHalfResolver = new StandardOutcomesResolver ( autoConfigurationClasses , split , autoConfigurationClasses . length , autoConfigurationMetadata , getBeanClassLoader ());
ConditionOutcome [] secondHalf = secondHalfResolver . resolveOutcomes ();
ConditionOutcome [] firstHalf = firstHalfResolver . resolveOutcomes ();
ConditionOutcome [] outcomes = new ConditionOutcome [ autoConfigurationClasses . length ] ;
System . arraycopy ( firstHalf , 0 , outcomes , 0 , firstHalf . length );
System . arraycopy ( secondHalf , 0 , outcomes , split , secondHalf . length );
return outcomes ;
}
这里为了加快筛选的速度,采用了多线程的去处理的做法,将读取到的自动配置分成了2个数组,主线程调用join的方式等待同步,加快处理速度。
在上面的resolveOutcomes()方法中会对条件进行过滤,一直跟着getOutcome()方法往下走,可以看到如下代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
private ConditionOutcome getOutcome ( String className , ClassLoader classLoader ) {
if ( ClassNameFilter . MISSING . matches ( className , classLoader )) {
return ConditionOutcome . noMatch ( ConditionMessage . forCondition ( ConditionalOnClass . class )
. didNotFind ( "required class" ). items ( Style . QUOTE , className ));
}
return null ;
}
从这里可以看出来,我们看到现在的代码只是对spring.factories中条件进行初步的过滤,对于我们看到的OnClasssCondtion,它只会保留满足ConditionalOnClass.class这种条件注解的自动配置。
后面才对进行我们最上面分析的其他条件注解的过滤。