接口中默认方法修饰为普通方法
JDK8之前
- 变量:
public static fianl修饰
- 方法:
public abstract
JDK8开始
Lambda表达式
使用Lambda表达式依赖于函数接口
-
在接口中只能有一个抽象方法
-
在函数接口中定义Object类中的方法
-
使用默认或者静态方法
-
@FunctionalInterface 标识该接口为函数接口,如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
/**
* 只有一个抽象方法
* 函数接口
*/
public interface MyFunctionalInterface {
void get();
}
|
如果在该接口上加上注解@FunctionalInterface,则该接口为中不能再有其他抽象方法,否则报错。若是有多个抽象方法,则使用Lambda表达式的时候无法知道调用哪一个方法
-
@FunctionalInterface标识的类中可以有default方法或者Object类中的方法,如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MyFunctionalInterface {
void get();
default void add(){
}
String toString();
}
|
Lambda表达式语法
() 参数列表-> 分割{} 方法体- 完整:
(a, b) -> {}
无参方法调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
@FunctionalInterface
public interface WuCanInterface {
void get();
}
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 匿名内部类
new WuCanInterface() {
@Override
public void get() {
System.out.println("get");
}
}.get();
// Lambda表达式
WuCanInterface wuCanInterface = () -> {
System.out.println("lambda get");
};
wuCanInterface.get();
// 精简Lambda表达式
// 方法体中只有一条 语句的时候,不需要写{}
((WuCanInterface)() -> System.out.println("精简 lambda表达式")).get();
}
}
|
有参方法调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
@FunctionalInterface
public interface YouCanInterface {
String get(int i, int j);
}
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 匿名内部类
YouCanInterface youCanInterface = new YouCanInterface() {
@Override
public String get(int i, int j) {
return i + "--" + j;
}
};
System.out.println(youCanInterface.get(1, 4));
// lambda表达式
YouCanInterface youCanInterface1 = (i, j) -> {
return i + "---" + j;
};
System.out.println(youCanInterface1.get(1, 5));
}
}
|
Lambda表达式部分应用
集合遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("B");
list.add("C");
list.add("A");
// 匿名内部类
list.forEach(new Consumer<String>() {
@Override
public void accept(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
});
// lambda表达式遍历
list.forEach(s -> {
System.out.println(s);
});
// 更精简
list.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
|
集合排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<UserEntity> userList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaoming", 10));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaogang", 8));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaohua", 15));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaoli", 5));
// 匿名内部类方法
userList.sort(new Comparator<UserEntity>() {
@Override
public int compare(UserEntity o1, UserEntity o2) {
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
}
});
userList.forEach(new Consumer<UserEntity>() {
@Override
public void accept(UserEntity userEntity) {
System.out.println(userEntity);
}
});
// lambda表达式方法
userList.sort((o1, o2) -> o1.getAge() - o2.getAge());
userList.forEach(userEntity -> {
System.out.println(userEntity);
});
// 更精简
userList.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(UserEntity::getAge));
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
|
线程调用
因为Runnable接口是函数接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 匿名内部类
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程名称: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", 子线程");
}
}).start();
// lambda表达式
new Thread(() -> System.out.println("线程名称: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", 子线程")).start();
}
}
|
Stream流
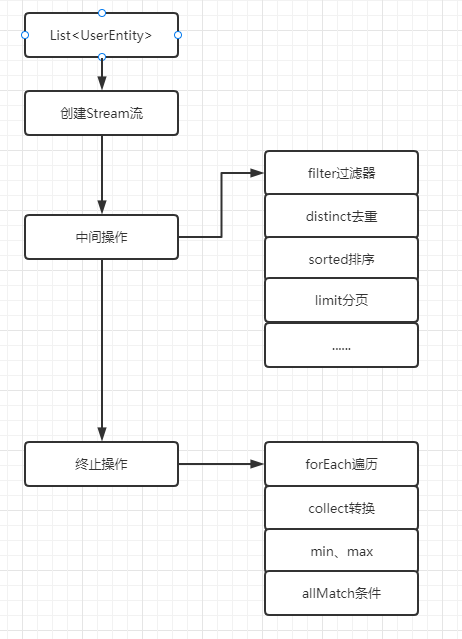
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<UserEntity> userList = new ArrayList<>();
// 创建方式有两种
// 第一种: 串行流
Stream<UserEntity> stream = userList.stream();
// 第二种:并行流
Stream<UserEntity> userEntityStream = userList.parallelStream();
}
}
|
Stream流部分应用
List集合转map
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<UserEntity> userList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaoming", 10));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaogang", 8));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaohua", 15));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaoli", 5));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaowang", 3));
// 创建方式有两种
// 第一种: 串行流
Stream<UserEntity> stream = userList.stream();
// 第二种:并行流
Stream<UserEntity> userEntityStream = userList.parallelStream();
Map<String, UserEntity> map = stream.collect(Collectors.toMap(new Function<UserEntity, String>() {
// 第一个泛型UserEntity是List中泛型的类型
// 第二个泛型String是将要转换的Map中key的类型
@Override
public String apply(UserEntity userEntity) {
// 该方法是key
return userEntity.getUsername();
}
}, new Function<UserEntity, UserEntity>() {
// 第一个泛型UserEntity是List中泛型的类型
// 第二个泛型UserEntity是将要转换的Map中value的类型
@Override
public UserEntity apply(UserEntity userEntity) {
// 该方法还value
return userEntity;
}
}));
map.forEach(new BiConsumer<String, UserEntity>() {
@Override
public void accept(String s, UserEntity userEntity) {
System.out.println(s + "----" + userEntity.getUsername());
}
});
// lambda表达式简化
Map<String, UserEntity> map2 = stream.collect(Collectors.toMap(UserEntity::getUsername, userEntity -> userEntity));
map.forEach((s, userEntity) -> System.out.println(s + "----" + userEntity.getUsername()));
}
}
|
计算求和
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(10, 20, 40, 60, 30);
Optional<Integer> reduce = stream.reduce(new BinaryOperator<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer apply(Integer num1, Integer num2) {
return num1 + num2;
}
});
System.out.println(reduce.get());
// lambda精简
reduce = stream.reduce(Integer::sum);
System.out.println(reduce.get());
// 对象
List<UserEntity> userList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaoming", 10));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaogang", 8));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaohua", 15));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaoli", 5));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaowang", 3));
Optional<UserEntity> reduceEntity = userList.stream().reduce(new BinaryOperator<UserEntity>() {
@Override
public UserEntity apply(UserEntity userEntity, UserEntity userEntity2) {
UserEntity reduceEntity = new UserEntity("reduce", 0);
reduceEntity.setAge(userEntity.getAge() + userEntity2.getAge());
return reduceEntity;
}
});
System.out.println(reduceEntity.get());
// lambda精简
reduceEntity = userList.stream().reduce((userEntity, userEntity2) -> {
UserEntity reduceEntity1 = new UserEntity("reduce", 0);
reduceEntity1.setAge(userEntity.getAge() + userEntity2.getAge());
return reduceEntity1;
});
System.out.println(reduceEntity.get());
}
}
|
查找集合最值元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<UserEntity> userList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaoming", 10));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaogang", 8));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaohua", 15));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaoli", 5));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaowang", 3));
// 最大值
Optional<UserEntity> max = userList.stream().max(new Comparator<UserEntity>() {
@Override
public int compare(UserEntity o1, UserEntity o2) {
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
}
});
System.out.println(max.get());
// lambda表达式方式
max = userList.stream().min(Comparator.comparingInt(UserEntity::getAge));
System.out.println(max.get());
// 最小值
Optional<UserEntity> min = userList.stream().min(new Comparator<UserEntity>() {
@Override
public int compare(UserEntity o1, UserEntity o2) {
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
}
});
System.out.println(min.get());
// lambda表达式方式
min = userList.stream().min(Comparator.comparingInt(UserEntity::getAge));
System.out.println(min.get());
}
}
|
判断集合是否存在某元素
allMatch:所有元素都满足返回trueanyMatch: 只要有满足一条满足,就返回true
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<UserEntity> userList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaoming", 10));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaogang", 8));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaohua", 15));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaoli", 5));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaowang", 3));
// 集合中是否存在
boolean xiaoming = userList.stream().anyMatch(new Predicate<UserEntity>() {
@Override
public boolean test(UserEntity userEntity) {
return userEntity.getUsername().equals("xiaoming");
}
});
System.out.println(xiaoming);
// lambda表达式形式
xiaoming = userList.stream().anyMatch(userEntity -> userEntity.getUsername().equals("xiaoming"));
System.out.println(xiaoming);
// 集合中的源素是否满足
xiaoming = userList.stream().allMatch(new Predicate<UserEntity>() {
@Override
public boolean test(UserEntity userEntity) {
return userEntity.getUsername().equals("xiaoming");
}
});
System.out.println(xiaoming);
// lambda表达式形式
xiaoming = userList.stream().allMatch(userEntity -> userEntity.getUsername().equals("xiaoming"));
System.out.println(xiaoming);
}
}
|
过滤器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<UserEntity> userList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaoming", 10));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaogang", 8));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaohua", 15));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaoli", 5));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaowang", 3));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaogang", 27));
userList.stream().filter(new Predicate<UserEntity>() {
@Override
public boolean test(UserEntity userEntity) {
// 这里可以添加多个条件
// 如还需要年龄要求 可以直接加 && userEntity.getAge > 10
return userEntity.getUsername().equals("xiaogang");
}
}).forEach(new Consumer<UserEntity>() {
@Override
public void accept(UserEntity userEntity) {
System.out.println(userEntity.toString());
}
});
// lambda表达式
userList.stream().filter(userEntity -> {
// 这里可以添加多个条件
// 如还需要年龄要求 可以直接加 && userEntity.getAge > 10
return userEntity.getUsername().equals("xiaogang");
}).forEach(userEntity -> System.out.println(userEntity.toString()));
}
}
|
limit和skip
skip:跳过n条limit:从第0条开始返回n条
可以联合使用skip和limit完成分页效果。
由于limit无法选择从第几条开始,只能限制返回几条,所以可以先使用skip跳过指定条数,再使用limit来限制需要返回的条数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public class Test06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<UserEntity> userList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaoming", 10));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaogang", 8));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaohua", 15));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaoli", 5));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaowang", 3));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaogang", 27));
// 输出xiaoli和xiaowang两条记录
userList.stream().skip(3).limit(2).forEach(userEntity -> {
System.out.println(userEntity.toString());
});
}
}
|
排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public class Test07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<UserEntity> userList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaoming", 10));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaogang", 8));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaohua", 15));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaoli", 5));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaowang", 3));
userList.add(new UserEntity("xiaogang", 27));
userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(UserEntity::getAge)).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
|
并行流
利用500亿以内的数累加求和来测试
-
串行流
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
public class Test08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Instant start = Instant.now();
long sum = 0;
for (long i = 0; i < 50000000000L; i++) {
sum += i;
}
System.out.println(sum);
Instant end = Instant.now();
System.out.println("【串行流】500亿累加求和用时:" + (Duration.between(start, end).toMillis()));
// 打印结果:
// -4378597037249509888
// 【串行流】500亿累加求和用时:11279
}
}
|
-
串行流
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public class Test09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Instant start = Instant.now();
LongStream longStream = LongStream.rangeClosed(0, 50000000000L);
OptionalLong result = longStream.parallel().reduce(new LongBinaryOperator() {
@Override
public long applyAsLong(long left, long right) {
return left + right;
}
});
System.out.println(result.getAsLong());
Instant end = Instant.now();
System.out.println("【并行流】500亿累加求和用时:" + (Duration.between(start, end).toMillis()));
// 打印结果
// -4378596987249509888
//【并行流】500亿累加求和用时:5416
}
}
|
采用多线程分段计算来增加计算速度。
fork join
对象判空
常用的API:
Optional.ofNullable()Optional.of()isPresent()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String username = null;
// 允许传递的对象为空
Optional<String> optional = Optional.ofNullable(username);
// 代码将在这一行抛出异常
String getUsername = optional.get();
System.out.println(getUsername);
String username1 = null;
// 不允许传递的对象为空
// 代码将在这一行抛出异常
Optional<String> optional2 = Optional.of(username1);
String getUsername1 = optional.get();
System.out.println(getUsername1);
// ofNullable和isPresent联合使用
// 优先判断是否为空
String username3 = null;
// 允许传递的对象为空
Optional<String> optional3 = Optional.ofNullable(username3);
// 如果username3为空,则返回false,否则返回true
boolean isPresent = optional.isPresent();
System.out.println(isPresent);
}
}
|
默认值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String username = null;
// 允许传递的对象为空
Optional<String> optional = Optional.ofNullable(username);
// 如果对象为空则使用默认值
String orElseUsername = optional.orElse("默认值");
System.out.println(orElseUsername);
}
}
|
条件过滤
-
filter()
返回值依然是Optional对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String username = "测试过滤";
// 允许传递的对象为空
Optional<String> optional = Optional.ofNullable(username);
// 如果对象为空则使用默认值
Optional<String> filter = optional.filter(new Predicate<String>() {
@Override
public boolean test(String s) {
return s.equals("测试过滤");
}
});
// 返回的依然是一个Optional
// 如果过滤结束此处没有值了,这里会报错
System.out.println(filter.get());
// lambda简化
Optional<String> filter1 = optional.filter(s -> s.equals("测试过滤"));
System.out.println(filter1.get());
}
}
|
案例
将给定对象一个属性字符串中的英文字符全部改成大写
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MessageEntity messageEntity = new MessageEntity("test01", "TEst01");
String result = Optional.ofNullable(messageEntity)
// messageEntity1 为前面传入的messageEntity
.map(messageEntity1 -> messageEntity.getMsg())
// message 为传入的messageEntity.getMsg()
.map(mesesage -> mesesage.toUpperCase(Locale.ROOT))
.orElse(null);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
|
